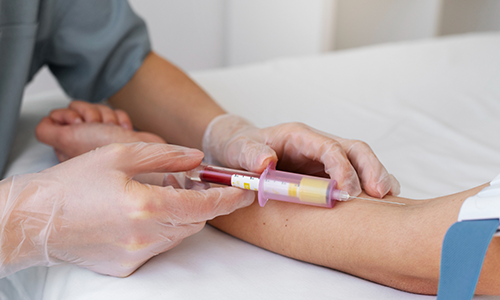
Hyperkalemia mean high protein, is the medical term which is used to describe the high level potassium in your than normal range. Potassium is a positive electrolyte that restrain the smooth and proper functioning of nerves system, muscle cells including those which are present in your heart. The normal range of potassium in your blood should be from 3.6 to 5.2 millimoles per liter. Having potassium higher than 6.o mmol/L require immediate treatment as it can be very dangerous.
Potassium is a positively charged electrolyte, electrolyte is mineral charged positively or negatively, it dissolves in our blood and helps carry electric charge throughout our body. It helps our body with the following functions -
• Expand and contract your muscle in the body
• Helps nerves send signal from brain to rest of the body and vice versa
• Moves nutrient in your cells and take out waste from the cells
• Offset the sodium effects in present in salt on your blood pressure
What are risks of hyperkalemia (high potassium)?
Now we will look into effects of high potassium in your blood. We get potassium from our food and drinks. Generally, kidney filters the excess potassium from our blood which leaves out through urine but if we have too much potassium in our it effect the functioning of kidney and it can’t filter out all of the excess potassium, which will build in our blood and potentially be the cause heart damage, weakening our muscles, makes us feel palpitations and because of heart attack.
What is normal range of potassium in your blood?
The normal range of potassium in your blood is from 3.6 to 5.2 millimoles per liter, potassium higher 6.0 mmol/L indicates a serious threat to your heart you need an immediate treatment.
How common is hyperkalemia?
The chances of hyperkalemia is two three times more among people with chronic kidney diseases. People with chronic kidney diseases but do not need dialysis tends to develops hyperkalemia.
Signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia:
People having mild hyperkalemia usually do not have any signs and symptoms of it or it is easy to dismiss those symptoms. Symptoms may develop over weeks and months of high potassium levels in your blood.
Mild hyperkalemia signs may include:
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Nausea or vomiting
A high potassium level over 6.0 mmol/L is very dangerous and can lead to heart damage, severe hyperkalemia signs may include:
• Chest pain
• Weakness and numbness of muscles in your limbs
• Arrhythmia
• Heart palpitations
Cause of hyperkalemia:
The most common cause of hyperkalemia is chronic kidney disease. Kidney disease damages the kidneys and it proper and smooth functioning of kidney means it can’t filter the extra potassium in your blood.
There are several factors which contribute to hyperkalemia are:
• High potassium rich diet
• Medication that resist the kidneys ability to filter the potassium which includes the certain drugs to treat high blood pressure.
Genetic disorder may cause high potassium level, which include:
Psedohypoaldosteronism type1 (PHA 1) - it is genetic mutation which helpd regulate sodium causes PHA1 in your body.
Psedohypoaldosteronism type2 (PHA 2) - PHA2 is also known as Gordon’s syndrome, it is a genetic mutation that helps regulate your blood pressure causes PHA2.
Risks:
People of any age group can have hyperkalemia including children, people with following diseases or health conditions are at higher risk of developing hyperkalemia are:
• Alcohol use disorder
• Severe burns on a large part of body
• Addison’s disorder
• Diabetes
• Congestive heart failure
• HIV
• Chronic kidney diseases or family history of it
• Abnormal kidney structure
Diagnosis:
In order to diagnose hyperkalemia, a serum potassium test can be very helpful. It is test that measures the potassium in your blood. As most people do not have any symptoms when doctor suggests to a test you can have it.
Electrocardiogram ( EKG ) is another option which can confirm the hyperkalemia, it shows tha changes in your heart rhythms. Tall T peaked waves suggests the early signs of hyperkalemia. T waves show your heart at rest after beating.